Bifurcated AI: The Transaction Architecture That Actually Scales

At this point in time, you are in a certain state. Your lean team is deploying AI with varying degrees of success. Maybe you're happy with the results. Maybe you are not. But like all things in life, the only certainty is the uncertainty of your evolution toward the next state.
Transaction friction happens when your current architecture doesn't match your actual needs. This mismatch appears most often in how teams deploy AI—applying sophisticated frameworks where simple ones would work, or lightweight approaches to mission-critical tasks.
Transaction = Current State → Desired State
The common misconception is that AI deployment should follow a unified pattern. After studying dozens of successful micro-teams, we've identified a different reality:
Successful AI deployment requires bifurcation—two fundamentally different transaction types with distinct architectures.
Let's examine this transaction architecture in detail.
The Two Transaction Modes
1. Precision Forces (High-Value Transactions)
These are your elite operations—expensive, mission-critical transactions where failure costs exceed deployment costs:
- Transaction terms: High resource investment, surgical precision, human oversight
- Value exchange: Trading latency and cost for reliability and impact
- Examples: Client deliverables, financial operations, strategic decisions
2. Volume Forces (Mass Transactions)
These are your scalable operations—low-cost, parallelizable transactions where some failures are acceptable:
- Transaction terms: Minimal resource cost, parallel execution, error tolerance
- Value exchange: Trading reliability for scale and throughput
- Examples: Data processing, content generation, research collection
This bifurcation borrows conceptually from military doctrine (particularly the "elite special forces" vs "conventional forces" model), where resource allocation differs dramatically based on mission criticality.
Where Most Teams Create Transaction Friction
The primary friction in AI deployment comes from the "muddy middle"—applying a single deployment pattern to all tasks regardless of their nature:
- Overengineered volume tasks: Using GPT-4 with complex retrieval for tasks where a simple prompt would suffice
- Underprovisioned precision tasks: Applying basic, unverified automation to mission-critical workflows
Current frameworks try blending these distinct transaction types and create failure modes in both directions.
The Bifurcated Architecture
1. Define Clear Intent
Begin every workflow by writing a clear transaction objective in 140 characters or less. This becomes the canonical intent that all subsequent operations must satisfy.
2. Select Transaction Type
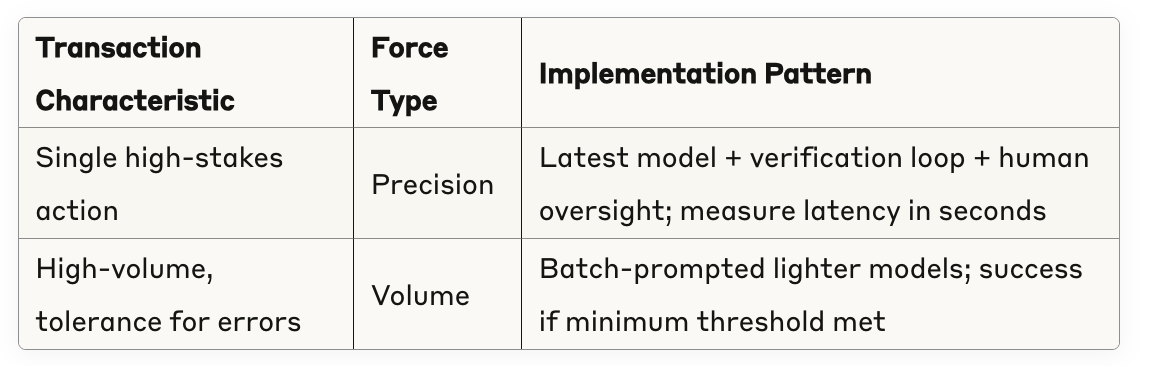
3. Set Appropriate Settlement Terms
Volume operations are pre-declared as negotiable transactions: if 30% of processes fail, the transaction can still be considered settled. Precision operations must be fulfilled transactions where any failure triggers immediate intervention.
4. Regular Transaction Hygiene
Unused scripts, stale prompts, inactive automations—these are neglected transactions creating drag on your system. Schedule weekly purges to eliminate them without ceremony.
Bootstrap Your Bifurcated Architecture By Friday
- Write one explicit intent statement—tweet length, single objective.
- Classify workflows as precision or volume. When uncertain, default to volume.
- Create a single precision operation for your most critical transaction; measure latency.
- Deploy a volume operation fleet for scale work; define acceptable failure rates.
- Schedule weekly hygiene of neglected transactions.
Transaction Insight
Are you wasting resources on low-value operations or applying insufficient verification to critical workflows? Evaluate each AI deployment through the lens of transaction criticality. The right architecture for each transaction type will reduce friction and accelerate your evolution to the next state.
Every single AI workflow in your organization should be categorized by transaction type. This simple bifurcation—applying the right deployment pattern to each transaction—will outperform any unified approach..




